Introduction
The FAR (Federal Aviation Regulations) Part 25 are a set of airworthiness standards for airplanes in the transport category. These regulations are generally difficult to understand due to the non-straightforward nature of the language used.
As a part of this study, the sections pertaining to stability and control FAR requirements were studied. The main aim of the study was to understand each requirement and propose a procedure to evaluate that particular requirement. The report starts off with the control requirements and the stability part is handled later. The analysis of each requirement has been started by elaborating in brief the main requirement of the regulation. Then an approach to evaluate the regulation has been proposed by considering the Regional Transport Aircraft (RTA-70) as the test case. The main focus of the study is to provide a generic process that may be used for the future transport aircrafts also. Interestingly the whole study used just basic flight mechanics equations to draft this process.
The FARs are quite fun to read and and would give an idea of the complex procedure through which an aircraft design has to go through. Refer to the following link for the complete set of FAR 25 standards: http://ecfr.gpoaccess.gov/cgi/t/text/text-idx?c=ecfr&rgn=div5&view=text&node=14:1.0.1.3.11&idno=14
Overview of Project
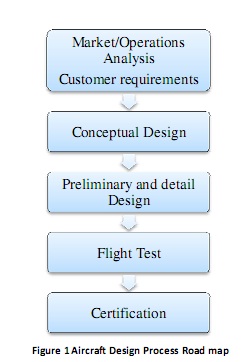
The above figure illustrates a general Aircraft Design Process. 'Certification' part is being focused at as a part of this project. As can be seen, certification is a very important part of aircraft design and drives the design to a certain extent. This is true especially in the case of stability and control system of the aircraft.
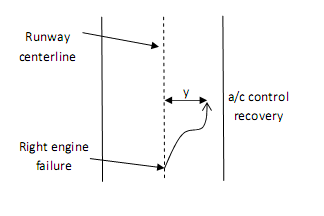
Without going into too much detail, I'll explain one of the regulations in brief. This should give an idea as to how these airworthiness standards make our flight 'safe'. One of the most critical cases which is considered is an engine failure during take-off. During take-off, the aircraft employs its wing flaps (for getting maximum lift). Suppose one of its engine fails, the pilot must be able to control the aircraft and bring it back to safety. Consider the following figure: