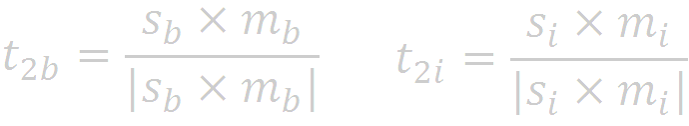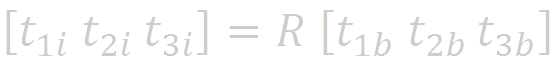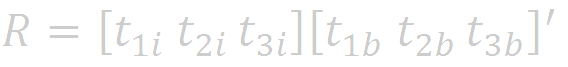Difference between revisions of "Triad Algorithm"
(Created page with "Triad is one of the simplest deterministic attitude determination algorithm. Triad begins by considering two measurement vectors, such as the direction to the sun and the dire...") |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
where []' indicates inverse of the matrix. <br \> | where []' indicates inverse of the matrix. <br \> | ||
With this, we have found an appropriate Rotation Matrix. <br \> | With this, we have found an appropriate Rotation Matrix. <br \> | ||
| − | Notice that in general, s and m may not be perpendicular. So if we directly used t_1 = s t_2 = m, the matrix we get by this method may not be orthogonal. When we construct orthogonal vectors from these, we are in effect reducing a constraint of the equation and making the equations solvable. | + | Notice that in general, s and m may not be perpendicular. So if we directly used t_1 = s and t_2 = m, the matrix we get by this method may not be orthogonal. When we construct orthogonal vectors from these, we are in effect reducing a constraint of the equation and making the equations solvable. |
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 10:18, 28 January 2018
Triad is one of the simplest deterministic attitude determination algorithm. Triad begins by considering two measurement vectors, such as the direction to the sun and the direction of the Earth's magnetic field. We denote the actual vectors by s and m, respectively. The measured components of the vectors, with respect to the body frame (A reference frame that is attached to the body of the satellite) , are denoted s_b and m_b, respectively. The known components of the vectors in the inertial frame are s_i and m_i. Ideally, the rotation matrix, or attitude matrix, R, satisfies ![]() and
and ![]() . Unfortunately, since the problem is overdetermined (the Rotation Matrix has three independent parameters and we have four constraints by these two equations), it is generally not possible to find such an R. The simplest deterministic attitude determination algorithm is based on discarding one piece of this information; however, this approach does not simply amount to throwing away one of the components of one of the measured vectors. The algorithm is known as the Triad algorithm, because it is based on constructing two triads of orthonormal unit vectors using the vector information that we have.
. Unfortunately, since the problem is overdetermined (the Rotation Matrix has three independent parameters and we have four constraints by these two equations), it is generally not possible to find such an R. The simplest deterministic attitude determination algorithm is based on discarding one piece of this information; however, this approach does not simply amount to throwing away one of the components of one of the measured vectors. The algorithm is known as the Triad algorithm, because it is based on constructing two triads of orthonormal unit vectors using the vector information that we have.
The Algorithm
The algorithm considers one vector measurement to be more accurate than the other. For example, suppose we could consider the sun vector to have more accurate components than the magnetic field vector. We consider the accurate vector to be our first vector of the triad.
Thus, ![]() and
and ![]()
The second vector we chose is perpendicular to both measured vectors;
Note that we are in effect assuming that the measurement of the magnetic field vector is less accurate than the measurement of the sun vector. If the magnetic field vector is more accurate, suitable changes should be made in the triad.
Finally the third vector of the triad is
Now, we construct two matrices by putting the t vector components into the columns of two 3 x 3 matrices. The two matrices are
Note that
Thus,
where []' indicates inverse of the matrix.
With this, we have found an appropriate Rotation Matrix.
Notice that in general, s and m may not be perpendicular. So if we directly used t_1 = s and t_2 = m, the matrix we get by this method may not be orthogonal. When we construct orthogonal vectors from these, we are in effect reducing a constraint of the equation and making the equations solvable.
References
- http://www.dept.aoe.vt.edu/~cdhall/courses/aoe4140/attde.pdf
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Triad_method
If you are done reading this page, you can go back to Attitude Determination and Control Subsystem