Simulation of Hypersonic Shock/Turbulent Boundary-Layer Interactions using Advanced Turbulence Models :
This article presents a numerical study of hypersonic shock-wave/boundary-layer interactions. Reynolds
averaged Navier-Stokes method using one-equation and two-equation turbulence models are solved for large cone/flare
configurations with well documented experimental data. These interactions can result in significant flow separation and
aero-thermal loads. The standard Spalart-Allmaras and k-omega models lack in predicting the correct size of separation
bubble size and show deviation in flow predictions and wall data. The shock-unsteadiness modifications of Sinha et al.
(Physics of fluids, 2003) show significant improvement in predicting the flow separation at the cone/flare junction.
The experimental shock-structure and wall data is also reproduced well. Keywords: shock-wave, turbulent boundary-layer,
shock-unsteadiness, separation bubble.
Ref: Pasha, Amjad A., Sinha, K., "Simulation of Hypersonic Shock/Turbulent Boundary-Layer Interactions using
Advanced Turbulence Models". 8th Asian Computational Fluid Dynamics Conference ,Hong Kong, 10-14 January, 2010.
Representative results:
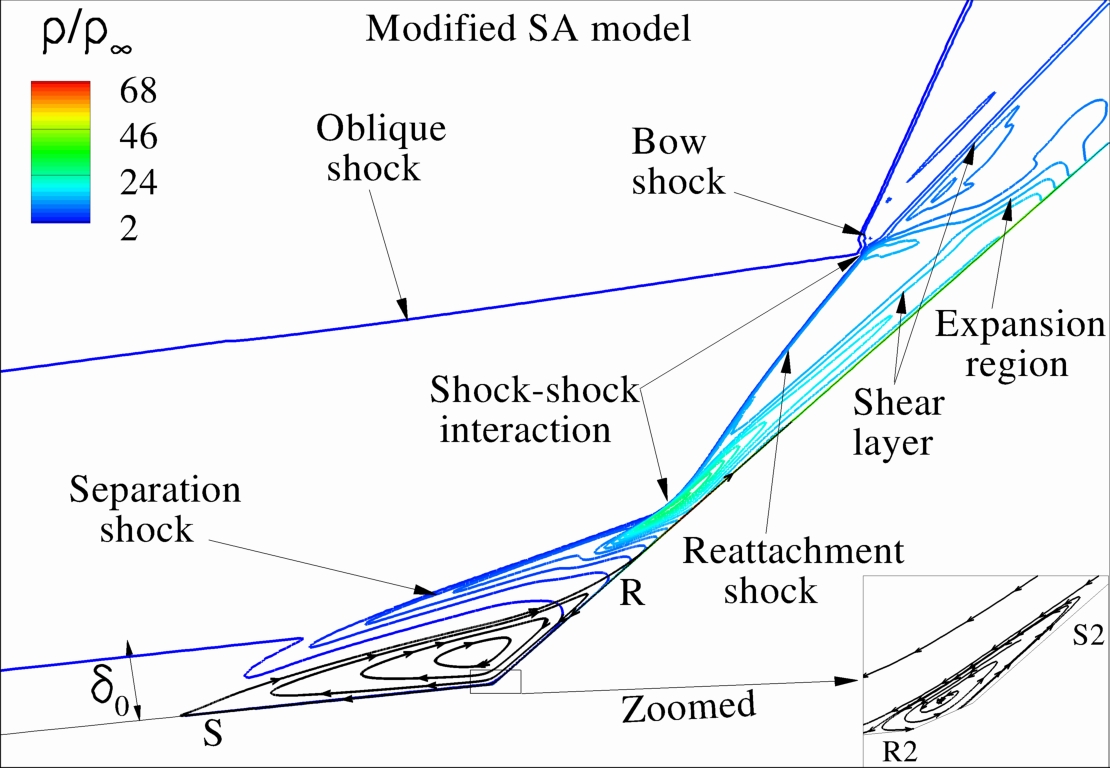
Shock structure in hypersonic shock/boundary layer interaction.
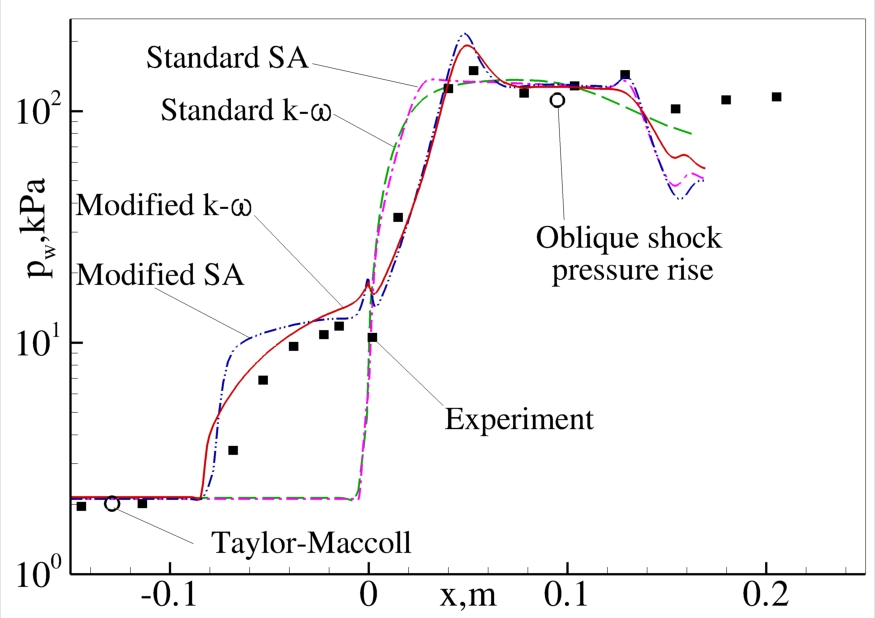
Comparison of CFD vs. experiment for surface pressure distribution.