Difference between revisions of "Negative-stiffness isolators"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
* '''Vertical Motion Isolation:''' | * '''Vertical Motion Isolation:''' | ||
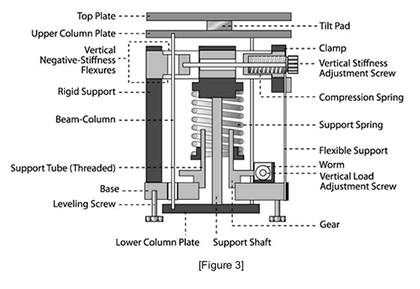
It uses a conventional spring connected to a Negative Stiffness Isolator (NSI) consisting of two bars hinged at the center. The stiffness of the isolator is K=KS-KN where KS is the spring stiffness and KN is the magnitude of a negative-stiffness which is a function of the length of the bars and the load P. | It uses a conventional spring connected to a Negative Stiffness Isolator (NSI) consisting of two bars hinged at the center. The stiffness of the isolator is K=KS-KN where KS is the spring stiffness and KN is the magnitude of a negative-stiffness which is a function of the length of the bars and the load P. | ||
| − | + | ||
* '''Horizontal Motion Isolation:''' | * '''Horizontal Motion Isolation:''' | ||
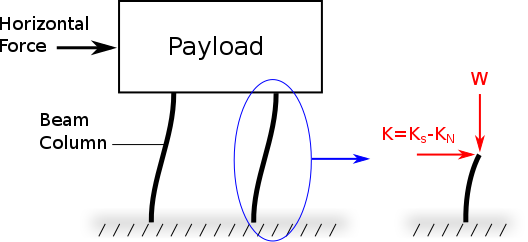
The beam-columns have horizontal stiffness Ks with the weight load applied laterally. Due to this the lateral bending stiffness is reduced by the "beam-column" effect. This behavior is equivalent to a horizontal spring combined with an NSI so that the horizontal stiffness is K=Ks-Kn, and Kn is the magnitude of the beam-column effect. | The beam-columns have horizontal stiffness Ks with the weight load applied laterally. Due to this the lateral bending stiffness is reduced by the "beam-column" effect. This behavior is equivalent to a horizontal spring combined with an NSI so that the horizontal stiffness is K=Ks-Kn, and Kn is the magnitude of the beam-column effect. | ||
[[File:NSI2.png|frame|left|Image reproduced from [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Vibrations_damping.svg here]]] | [[File:NSI2.png|frame|left|Image reproduced from [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Vibrations_damping.svg here]]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[File:NSI5.gif|frame|center|Image reproduced form [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Vibrations_damping.svg here]]] | [[File:NSI5.gif|frame|center|Image reproduced form [https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Vibrations_damping.svg here]]] | ||
<br \> | <br \> | ||
Revision as of 22:08, 20 February 2018
- Natural frequency range: 0.17 – 2.5 Hz
- Vertical Motion Isolation:
It uses a conventional spring connected to a Negative Stiffness Isolator (NSI) consisting of two bars hinged at the center. The stiffness of the isolator is K=KS-KN where KS is the spring stiffness and KN is the magnitude of a negative-stiffness which is a function of the length of the bars and the load P.
- Horizontal Motion Isolation:
The beam-columns have horizontal stiffness Ks with the weight load applied laterally. Due to this the lateral bending stiffness is reduced by the "beam-column" effect. This behavior is equivalent to a horizontal spring combined with an NSI so that the horizontal stiffness is K=Ks-Kn, and Kn is the magnitude of the beam-column effect.
If you are done reading this page, you can go back to Types of PVI Systems
References
This page has been inspired from https://www.minusk.com/content/in-the-news/Cleanroom_Technology_0412.html